

No reduction is needed, however the patient would benefit from procedural sedation for application of the castĪbove-knee cast for 4-6 weeks (age-and healing-dependent), non-weight bearing. What is the usual ED management for this injury? unable to achieve or maintain reduction (including if ED is not experienced in fracture reduction, splinting or casting)ġ0.

Indications for prompt consultation include: Table 1: Acceptable reduction parameters.ĩ. The majority will require closed reduction.ĪP and lateral radiographs of the tibia, including the knee and ankle joints should be obtained immediately after reduction to verify alignment. Reduction is required with any displaced fracture. When is reduction (non-operative and operative) required? The fibula fracture is located in the proximal third. The tibial shaft fracture is located in the distal third. Thus when casting this fracture the cast should be moulded into slight valgus to protect against this.įigure 4: AP and lateral x-ray of tibia and fibula shaft. Most tibial shaft fractures are short oblique or transverse fractures of the middle or distal third.įigure 3: With an intact fibula it will tend to push the tibia into varus during healing. Undisplaced complete isolated fracture of tibial shaftįigure 2: Undisplaced complete isolated fracture of the tibial shaft.B) Radiographic evidence may only become apparent 7-10 days after the initial injury when new periosteal bone formation occurs (white arrow). When routine radiographs are normal but a fracture is suspected, oblique views may help visualise the fracture line. A) AP and lateral x-ray of a 15 month old boy who refused to weight bear. What do they look like on x-ray?įigure 1: Toddler fractures are often radiographically normal on initial x-ray. What radiological investigations should be ordered?Īnteroposterior (AP) and lateral x-rays of the tibia and fibula to include knee and ankle joints should be ordered.
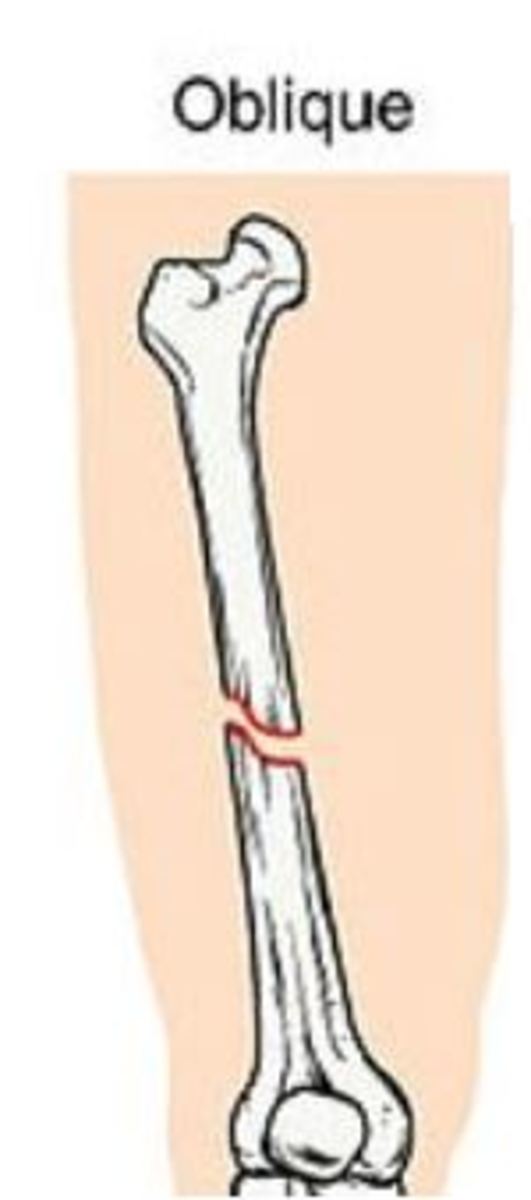
Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis should be excluded. These fractures occur as a result of a twisting injury. The periosteum remains intact and the bone is stable. A toddler's fracture is a spiral or oblique undisplaced fracture of the distal shaft of the tibia with an intact fibula. Toddler fractures occur in young ambulatory children (from 9 months to 3 years). The child will not want to weight bear on the injured leg. The child will present with pain, swelling and/or deformity in the lower leg. Thirty percent of tibial shaft fractures are associated with a fibula fracture Direct trauma frequently produces a transverse fracture or segmental fracture pattern, whereas rotational forces typically result in an oblique or spiral fracture. Tibial shaft fractures are the third most common long bone fracture in children and adolescents.įractures of the shaft of the tibia can result from a direct blow or a rotational force. How common are they and how do they occur? fracture pattern - transverse, spiral/oblique, comminuted or openĬ). location - proximal, middle, or distal thirdī). Tibial shaft (diaphyseal) fractures can be classified by:Ī). Unstable fractures may require general anaesthesic, manipulation and plaster GAMP) or fixation in theatre Patient would benefit from procedural sedation for application of the castĭisplaced tibial shaft fracture + / - fibular shaft fractureĬlosed reduction with above-knee cast for 4-6 weeks (age and healing-dependent), non-weight bearing Above-knee cast for 4-6 weeks (age and healing-dependent) An above-knee walking cast for 4 weeks is optional


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
